Space Force enlisted ranks largely mirror those of the Air Force. Space Force personnel are organized into two main groups: enlisted service members (E-1 to E-9) and commissioned officers (O-1 to O-10). All are known as Guardians.
Enlisted Guardians, who participate in and support operations, make up about half of the service. Each member has their own specialized training and fills a specific job role. Enlisted Guardians perform much of the technical and operational work that keeps the Space Force running – from satellite operations to cyber defense and support functions. As they rise into the noncommissioned officer (NCO) and senior NCO ranks, they also take on leadership, training and mentoring responsibilities.
Space Force officers, who plan and manage personnel, make up about half the service due to the fact that at its formation, the Space Force was primarily staffed with officers.Commissioned officers focus on strategy, mission planning and command. They oversee operations, make higher-level decisions and guide the force. Officers typically commission through ROTC, Officer Training School or the U.S. Air Force Academy, which also serves the Space Force.
Space Force Enlisted Ranks
Shortly after the Space Force’s creation in 2019, new members were recruited from airmen in the Air Force's space systems operations (1C6) career field.
Like the Air Force, enlisted Space Force ranks are broken down into three levels:
- Specialists (E-1 through E-4)
- Noncommissioned officers (E-5 and E-6)
- Senior noncommissioned officers (E-7 through E-9)
Then there is the chief master sergeant of the Space Force, designated by the E-9S rank.
Like the Air Force, the Space Force grants NCO status beginning at the grade of E-5 – earlier than in most other branches. Guardians with college credits or Junior ROTC experience may be able to enlist at an advanced grade, up to specialist 3 (E-3).

Space Force Ranks: Specialist (E-1 through E-4)
Specialist 1 (E-1)
Generally, Guardians graduate basic military training with the rank of Specialist 1 (E-1). At this stage, they are apprentices learning the basics of the military, including customs and Space Force values.
Specialist 2 (E-2)
The rank of Specialist 2 brings with it the responsibility of adjusting to the way of military life, and becoming proficient in their Space Force occupational specialty. In the Space Force, these fields are called Space Force Specialty Codes (SFSCs), the equivalent of the Air Force’s AFSCs. Guardians enter technical schools after basic training to gain proficiency in areas such as orbital warfare, cyber operations, space systems or intelligence, depending on aptitude, training opportunities and the needs of the service.
Specialist 3 (E-3)
By the rank of Specialist 3, Guardians are considered fully adjusted to the Space Force way of life. Their duties center on carrying out assigned missions effectively while sharpening both technical expertise and professional conduct.
Specialist 3s are expected to uphold Space Force standards consistently and begin demonstrating leadership qualities within their peer group. They also start refining their specialized skills to contribute meaningfully to operational units.
Specialist 4 (E-4)
The rank of Specialist 4 serves as a transition point from apprentice and journeyman-level responsibilities toward future leadership. Guardians at this stage are expected to show initiative, reliability and growing technical mastery, while also modeling professional behavior for newer Guardians.
Specialist 4s are encouraged to pursue professional development and leadership preparation, as they represent the image of competence, integrity and commitment to the Space Force mission.

Space Force Ranks: Noncommissioned Officer (NCO) (E-5 and E-6)
Enlisted Guardians at the ranks of Sergeant (E-5) and Technical Sergeant (E-6) are recognized as noncommissioned officers (NCOs). NCOs bridge the gap between junior enlisted Guardians and senior leadership. They are responsible not only for technical expertise in their specialties but also for shaping unit culture, modeling discipline and ensuring mission success in space and cyber operations.
The Space Force Personnel Management Act (PMA) established a board-based process for enlisted promotions rather than relying on the Weighted Airman Promotion System (WAPS) that the Air Force uses. Guardians are promoted through a central evaluation board system that combines time in grade (TIG)/time in service (TIS)/skill level eligibility with board reviews of records, performance and leadership potential.
Sergeant (E-5)
The entry point of the NCO tier, sergeants are expected to demonstrate technical expertise and emerging leadership capability. At this grade, Guardians begin to assume direct supervisory responsibilities for junior enlisted personnel.
Moving up in the Space Force ranks: For sergeant, selectees' average time in grade was about one year and time in service was 3.38 years, the Space Force said in July 2025.
Technical Sergeant (E-6)
Technical sergeants are recognized as seasoned technicians and supervisors who combine advanced technical proficiency with expanded leadership responsibilities.
Moving up in the Space Force ranks: Advancement to technical sergeant follows the same competitive standards used for sergeant, but with higher eligibility standards. For technical sergeant, selectees' average time in grade was 3.39 years and time in service was eight years, the Space Force said in July 2025.

Space Force Senior Noncommissioned Officer (SNCO) Ranks (E-7 through E-9)
Senior Noncommissioned Officers (SNCOs) are entrusted with maintaining the highest standards of integrity, leadership, loyalty and technical excellence, while serving as key mentors, managers and advisers in the force.
Master Sergeant (E-7)
The Master Sergeant (MSgt) is the first tier of the SNCO ranks. Guardians at this grade function as both technical experts and advanced leaders. Master sergeants carry significantly expanded responsibilities, requiring a broad operational perspective that blends technical mastery with managerial oversight.
Moving up the Space Force ranks: Promotion is determined through a competitive process. For master sergeant, selectees' average time in grade was 4.02 years and time in service was 12.48 years, the Space Force said in July 2025.
Senior Master Sergeant (E-8)
The Senior Master Sergeant (SMSgt) serves primarily as a superintendent and manager. At this level, broad management and leadership skills are essential, as SMSgts are expected to oversee large teams, manage resources and ensure readiness across their units.
Moving up the Space Force ranks: Advancement to senior master sergeant is among the most competitive transitions in the enlisted structure. Promotions are based on performance, leadership, breadth of experience, education and overall mission impact.
Chief Master Sergeant (E-9)
The Chief Master Sergeant (CMSgt) serves in the capacity of senior enlisted advisers, managers and mentors.
Moving up the Space Force ranks: Promotion is based on a highly selective process that places emphasis on leadership impact, mission contributions and overall readiness.
Chief Master Sergeant of the Space Force (CMSSF)
The Chief Master Sergeant of the Space Force (CMSSF) is the highest enlisted rank in the service. Appointed by the Chief of Space Operations (CSO), the CMSSF serves as the senior enlisted adviser to both the CSO and the secretary of the Air Force. The CMSSF represents the interests of the entire enlisted force at the highest levels of the Department of the Air Force, the Department of Defense and the U.S. government.
This position carries unique responsibilities for shaping enlisted policy, guiding force development and ensuring the welfare, readiness and effectiveness of all Guardians.
Space Force Commissioned Officer Ranks
Commissioned officers in the United States Space Force are entrusted with leading Guardians and ensuring that the service achieves its operational and strategic objectives.
The officer rank structure follows the same grade progression as other U.S. armed services, divided into three categories:
- Company grade officers (O-1 to O-3)
- Field grade officers (O-4 to O-6)
- General officers (O-7 to O-10)
Space Force Officer Ranks: Company Grade
These junior officers serve in direct leadership and developmental roles, focusing on mission execution, technical expertise and the supervision of small teams.
Second Lieutenant (2nd Lt) (O-1)
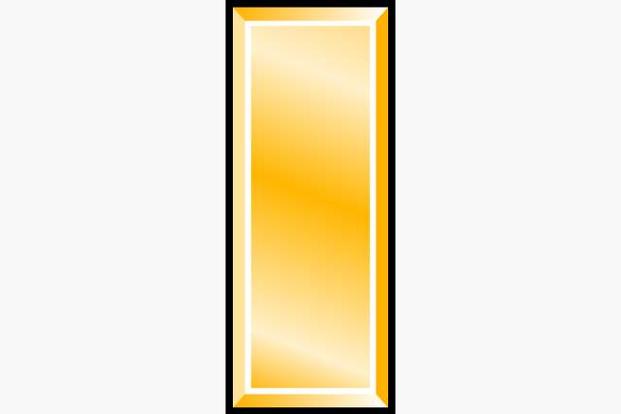
The entry-level commissioned officer rank, denoted by a single gold bar. Proper forms of address are “second lieutenant” or “lieutenant.”
First Lieutenant (1st Lt) (O-2)

They have responsibilities similar to a second lieutenant, but they get more duties, broader leadership responsibilities and higher pay.
Captain (Capt) (O-3)
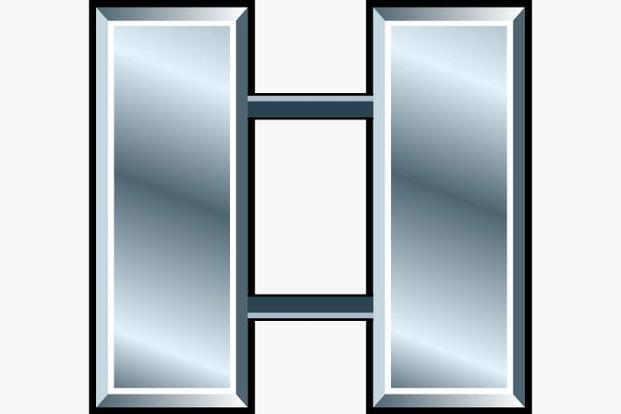
The highest company grade officer rank, denoted by two connected silver bars.
Space Force Field Grade Officers
These mid-level leaders assume responsibility for larger units, broader mission planning and operational management, often holding command positions at the squadron or group level.
Major (Maj) (O-4)
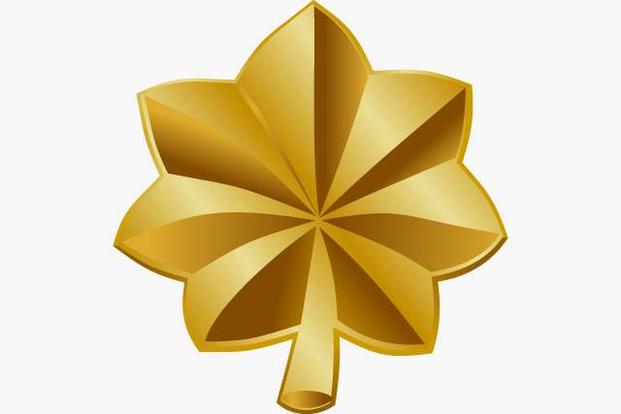

Officers promoted to major enter the first tier of field grade leadership. They typically serve in staff or operational roles requiring advanced expertise, integrating technical knowledge with leadership responsibilities.
Lieutenant Colonel (Lt Col) (O-5)
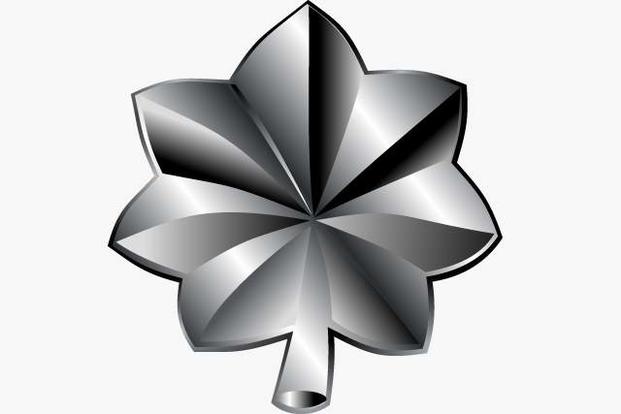

Lieutenant colonels serve in mid-level command and senior staff positions. They may be selected for squadron-level or equivalent commands within Space Force organizations, or provide senior expertise in operational planning and management.
Colonel (Col) (O-6)

Colonels occupy senior command and leadership positions. In the Space Force structure, colonels often lead Deltas, which are operational units responsible for mission areas such as orbital warfare, space domain awareness or cyber operations. They may also serve as senior staff leaders in headquarters and functional commands.
Space Force Officer Ranks: General Officers
Senior leaders who provide strategic vision, oversee major commands and direct the long-term development and readiness of the Space Force.
Brigadier General (Brig Gen) (O-7)

Becoming a brigadier general is an arduous process. It begins with a board of general officers creating a list of candidates and ends with the president choosing those to be promoted from that pool. Brigadier generals must retire after 30 years of service or after five years in their rank.
Major General (Maj Gen) (O-8)

A two-star general officer responsible for commanding large operational units, space mission portfolios or senior staff divisions. Promotion follows a similar process as brigadier general.
Lieutenant General (Lt Gen) (O-9)

A three-star general officer responsible for major commands, strategic operational sectors or top-level staff leadership. They are nominated from the pool of existing general officers and confirmed by the Senate. They advise senior leadership on policy, strategy and force readiness.
General (Gen) (O-10)

The highest standard general officer rank in the Space Force, the officer at this four-star level commands major areas of responsibility or serves in key positions at the Pentagon. Selection is highly competitive and requires nomination by the president and Senate confirmation. Generals provide overarching strategic direction, set priorities for the service and represent the Space Force in interagency and joint military operations.
Space Force Rank and Insignia
Enlisted Space Force Ranks
- E-1 – Guardian Basic (GB)
- E-2 – Guardian (Gd)
- E-3 – Guardian First Class (G1C)
- E-4 – Senior Guardian (SGd)
- E-5 – Sergeant (SSgt)
- E-6 – Technical Sergeant (TSgt)
- E-7 – Master Sergeant (MSgt)
- E-8 – Senior Master Sergeant (SMSgt)
- E-9 – Chief Master Sergeant (CMSgt)
- E-9S – Command Chief Master Sergeant (CCM)
- E-9S – Chief Master Sergeant of the Space Force (CMSSF)
Commissioned Officer Ranks
- O-1 – Second Lieutenant (2nd Lt)
- O-2 – First Lieutenant (1st Lt)
- O-3 – Captain (Capt)
- O-4 – Major (Maj)
- O-5 – Lieutenant Colonel (Lt Col)
- O-6 – Colonel (Col)
- O-7 – Brigadier General (Brig Gen)
- O-8 – Major General (Maj Gen)
- O-9 – Lieutenant General (Lt Gen)
- O-10 – General (Gen)
Interested in Joining the Military?
We can put you in touch with recruiters from the different military branches. Learn about the benefits of serving your country, paying for school, military career paths, and more: sign up now and hear from a recruiter near you.
















